Rail-mounted container gantry cranes are indispensable and highly efficient loading and unloading equipment in modern ports and logistics centers, and their importance is self-evident. With outstanding performance and a wide range of application scenarios, these cranes play a crucial role in improving logistics efficiency and reducing operational costs. This manual aims to provide a comprehensive introduction to the product features, structural composition, installation and commissioning, operating instructions, safety regulations, and maintenance of rail-mounted container gantry cranes, helping users quickly get started and maximize the equipment’s performance. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced operator, you can gain valuable reference information from this manual to ensure the safe and efficient operation of the equipment.
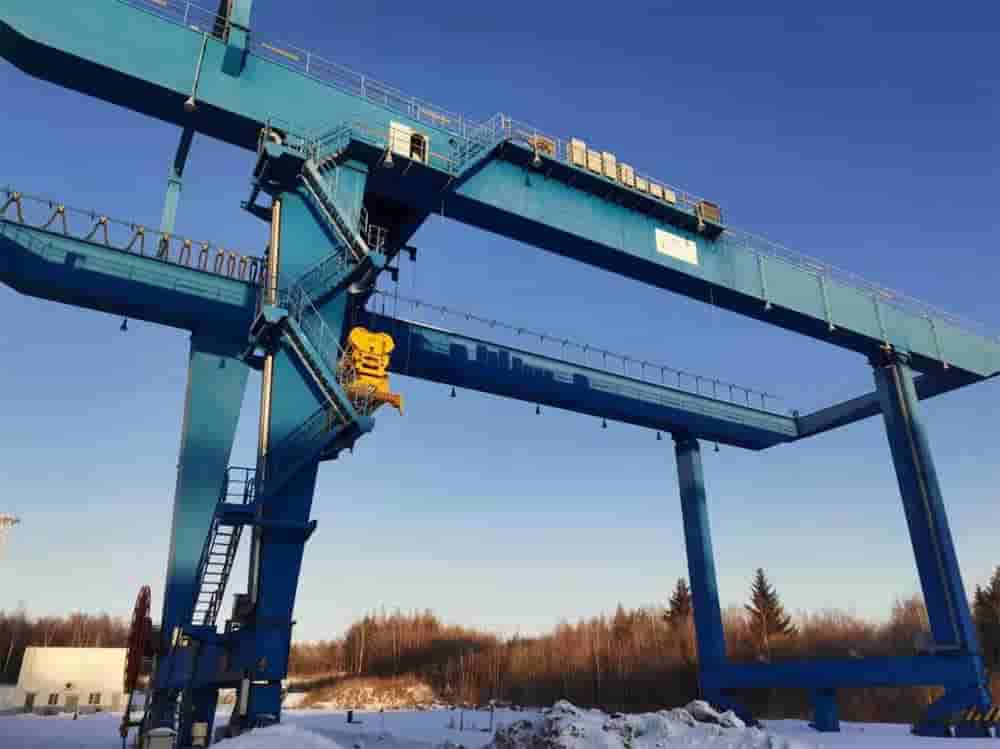

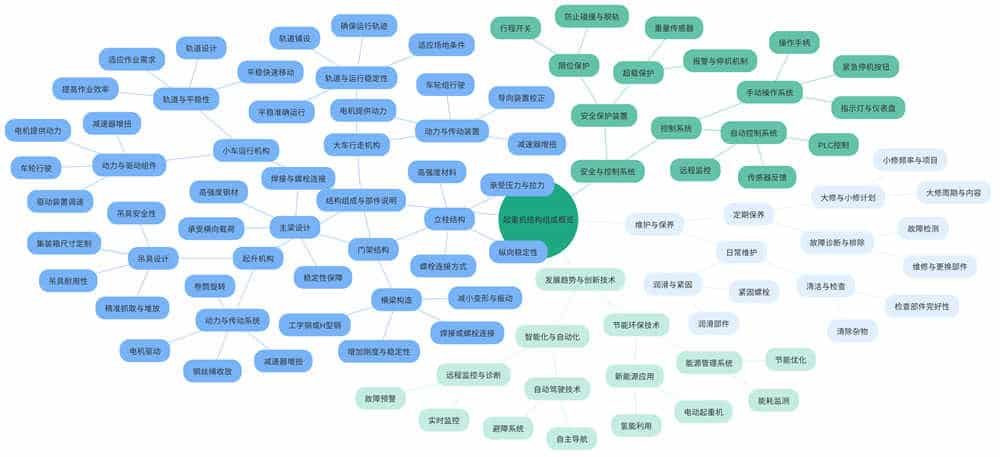
Rail-mounted container gantry cranes, commonly referred to as rail gantry cranes, are high-efficiency lifting equipment specifically designed for container terminals, logistics parks, and large storage facilities. These cranes feature a robust gantry structure and move along dedicated tracks to achieve precise horizontal movement, enabling efficient and safe loading, unloading, stacking, and transferring of containers. By combining advanced mechanical design principles with modern automation technology, rail gantry cranes significantly enhance container handling efficiency and ensure operational accuracy.
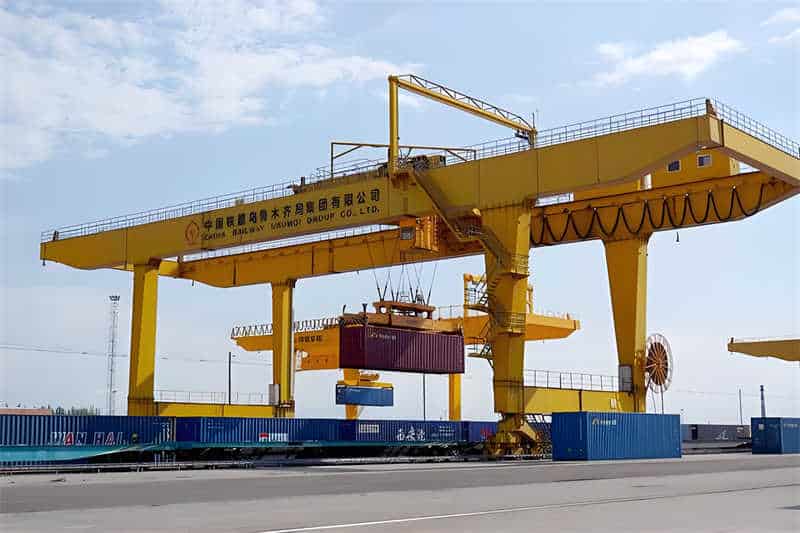
Rail-mounted container gantry cranes are equipped with several core functions, including container grabbing, lifting, transporting, and precise positioning and stacking. Their grabbing devices can accommodate containers of different sizes and weights, enabling rapid transfer and stacking within the yard through lifting and transporting operations. With their powerful lifting capacity and flexible operation, rail gantry cranes play a vital role in the logistics transportation system. They are widely used in seaports, river ports, railway freight yards, highway transfer stations, and large storage logistics centers, making them an indispensable key equipment in modern logistics transportation systems.
The technical specifications of rail-mounted container gantry cranes include lifting capacity, span, lifting height, and operating speed, among others. Lifting capacity, a critical parameter for crane performance, can be customized based on actual needs, ranging from tens to hundreds of tons. The span is designed according to the width of the site, typically reaching several tens of meters. The lifting height is determined based on the yard height and operational requirements, often reaching several tens of meters. Operating speed, including lifting speed, trolley travel speed, and gantry travel speed, is also a key factor affecting operational efficiency and is optimized to meet the demands of high-efficiency operations.
The gantry, as the core main structure of the rail-mounted container gantry crane, is designed and manufactured with consideration for mechanical strength, structural rigidity, and overall stability. The main beam is made of high-strength steel through welding or bolted connections, ensuring it can withstand the lateral loads generated during crane operations, such as the weight of containers and the loads from the lifting mechanism and trolley travel mechanism. It also maintains stable performance under extreme conditions like strong winds and earthquakes. The columns, key components supporting the main beam and maintaining its stability, are also made of high-strength materials and fixed to the ground or embedded parts through bolted connections. They must withstand significant vertical pressure and horizontal tension while ensuring the overall longitudinal (track direction) stability of the gantry. The crossbeam connects the two columns, forming a stable gantry structure. Typically made of I-beams or H-beams, the crossbeam is welded or bolted between the two columns. Its primary function is to enhance the gantry’s rigidity and stability while reducing deformation and vibration caused by lateral loads.
The lifting mechanism is a critical part of the container gantry crane, responsible for the vertical lifting of containers. It consists of a motor, reducer, drum, wire rope, and spreader. The motor serves as the power source, driving the drum’s rotation through the reducer, which reduces speed and increases torque. The drum is wound with wire rope, and the lifting and lowering of containers are achieved by retracting or releasing the wire rope. The spreader is a specialized tool customized according to the actual container size, ensuring precise grabbing and stacking.
The trolley travel mechanism is installed on the gantry’s main beam and is responsible for the horizontal movement of containers. It consists of a motor, reducer, wheels, and a drive device, enabling smooth and rapid movement along the track. The trolley travel speed can be adjusted according to operational requirements to meet efficiency needs in different scenarios. The motor provides power, which is transmitted through the reducer to reduce speed and increase torque, driving the wheels to move along the track. The drive device can adjust the trolley’s travel speed to adapt to various operational needs and site conditions.
The gantry travel mechanism is installed on the track and is responsible for the longitudinal movement of the entire crane. It consists of a motor, reducer, wheel set, and guiding device, ensuring smooth and accurate movement of the crane along the track. The gantry travel speed can also be adjusted according to operational requirements to adapt to different site conditions. The motor provides power, which is transmitted through the reducer to reduce speed and increase torque, driving the wheel set to move along the track. The guiding device ensures the crane maintains the correct trajectory and direction during operation.
Before installing the rail-mounted container gantry crane, a detailed site survey must be conducted. Ensure that the site is level, free from large pits or bumps, as these may affect the installation and performance of the equipment. Additionally, inspect all components to ensure they are intact and undamaged, including the tracks, gantry, lifting mechanism, trolley travel mechanism, and gantry travel mechanism. Prepare the necessary installation tools and safety protection equipment. The installation team must possess the appropriate qualifications and experience to ensure a smooth installation process and avoid equipment damage or safety accidents due to improper operations.
The installation process includes gantry assembly, track laying, and the installation and commissioning of the lifting mechanism, trolley travel mechanism, and gantry travel mechanism. During installation, strictly follow the installation drawings and instructions provided by the manufacturer. Ensure that all components are properly installed and securely connected. At the same time, pay attention to safe operations. For example, during hoisting, ensure the safe use of slings, hooks, and other lifting tools; during electrical installation, pay attention to the safe connection and protection of electrical circuits, etc., to avoid accidents.
After installation, systematic commissioning and testing are required. This includes no-load test runs, full-load test runs, and performance indicator tests. The no-load test run primarily checks whether all parts of the equipment operate smoothly and normally; the full-load test run checks whether the equipment can operate normally under full load; and the performance indicator tests verify whether the equipment’s performance parameters meet the design requirements. During the commissioning process, closely monitor the equipment’s operating status and promptly identify and address potential issues. After testing, ensure that all performance indicators of the equipment meet the design requirements before putting it into formal use.
Before starting, operators must conduct a comprehensive pre-start inspection of the equipment in strict accordance with safety regulations. First, ensure that the power supply is stable and reliable, all control circuits are intact, and safety protection devices such as overload protection and emergency stop buttons are functioning properly. After completing all necessary safety checks, press the start button and closely observe the startup and operation of all components, including the motor, hydraulic system, and electrical control system, to ensure they operate according to the preset program without abnormal noises or vibrations.
Once all systems of the crane are fully started and running stably, lifting operations can begin. During operations, continuously monitor the indicators on the instrument panel. If any abnormalities are detected, immediately stop the operation and investigate the issue. After completing the operation, move the crane to a safe position following the correct shutdown sequence, then disconnect the power supply and lock the control panel to ensure the equipment is completely stopped and in a safe state.
Before lifting operations, operators must accurately select and adjust the spreader position based on the size and weight of the container to ensure a proper fit and precise grabbing. During the lifting process, operators must constantly monitor the lifting height and speed to avoid collisions with buildings, equipment, or other facilities, which could cause damage or safety accidents.
During transportation, operators should maintain smooth operation to prevent the container from falling or being damaged due to sudden stops or starts. Additionally, always pay attention to the stacking position and stability of the container to ensure it is neatly and securely stacked. In case of emergencies or equipment malfunctions, immediately stop the operation and perform an emergency shutdown following the correct sequence.
During operations, if an emergency or equipment malfunction occurs, operators must immediately press the emergency stop button, cut off the power supply, and ensure the equipment safely stops running. During fault handling, conduct a comprehensive inspection of the equipment, including the electrical system, mechanical components, and safety protection devices, to ensure no safety hazards exist before resuming use.
For common electrical and mechanical faults, operators should be familiar with troubleshooting and repair methods to quickly restore normal operation. Additionally, regular maintenance, including lubrication, cleaning, tightening, and adjustments, is necessary to extend the equipment’s service life.
Daily inspections are crucial to ensuring the crane’s normal operation. Operators must conduct a thorough inspection of the crane’s exterior, electrical system, mechanical components, and safety protection devices. Exterior inspections include checking for wear, deformation, cracks, and other issues. Electrical system inspections involve verifying the integrity of control circuits and the proper functioning of electrical components. Mechanical component inspections include checking the transmission mechanism, hydraulic system, and lubrication system. Safety protection device inspections ensure that overload protection, emergency stop buttons, and other safety features are functioning correctly.
Furthermore, operators must perform regular maintenance, including lubrication, cleaning, tightening, and adjustments. Lubrication is essential for smooth operation and should be applied to all relevant parts regularly. Cleaning ensures the equipment’s exterior and interior remain free of debris. Tightening ensures all connections are secure, and adjustments ensure all components operate correctly.

Operators must undergo rigorous selection and training to ensure they possess the necessary professional knowledge and practical experience related to the equipment. This includes a deep understanding of the equipment’s basic principles, structural design, and performance, as well as proficiency in operating skills. Before being allowed to operate the equipment independently, all operators must complete systematic professional training and pass strict assessments to verify their ability to perform tasks accurately and efficiently. Additionally, operators are required to participate in regular safety training and reviews to continuously improve their professional skills and safety awareness.
Maintaining a clean and orderly work environment is a critical prerequisite for safe operations. Operators must promptly clear debris from the work area to avoid obstructions and safety hazards caused by clutter. For heavy equipment like rail-mounted cranes, in addition to daily maintenance to ensure the tracks are level, free from deformation, damage, or debris, regular inspections and corrections are necessary to ensure the track system remains in good condition, guaranteeing the crane’s smooth operation. To further enhance safety management, clearly marked safety warning signs, such as boundary warning tapes, warning lights, and signs, should be installed to alert personnel. Additionally, based on the work content and risk assessment results, appropriate protective devices such as guardrails, safety nets, and fall protection systems should be installed and used to ensure the safety of personnel and equipment during operations.
During operations, operators must strictly adhere to pre-established safety operation procedures and avoid any violations. This requires operators to remain fully focused and cautious, continuously monitoring the equipment’s operating status and any subtle changes in the surrounding environment. If any potential safety hazards are detected, such as abnormal equipment components, deteriorating work conditions, or unexpected obstacles, operators must immediately stop the operation and take appropriate measures to address or avoid the issue, ensuring the safety and smooth progress of the operation.
Detailed emergency response plans should be developed for potential emergencies, such as equipment malfunctions, fires, or personnel injuries. These plans must outline specific response procedures, responsibilities, and rescue measures to ensure rapid and effective handling of emergencies, minimizing losses to the greatest extent possible.
Comparison table of key points of safety operation procedures
| Key points of the procedure | Specific content |
| Operator qualifications | After strict selection and training, professional knowledge and practical experience, and pass assessment and evaluation |
| Regularly participate in safety training and review to improve professional skills and safety awareness | |
| Safe working environment | The work site is clean and orderly, and the debris is cleaned in time |
| The tracks of heavy equipment such as rail cranes are flat, without deformation, damage or debris, and regular inspection and calibration | |
| Set up standardized and eye-catching safety warning signs, such as boundary warning belts, warning lights, warning signs, etc. | |
| Reasonable configuration and use of protective equipment, such as protective barriers, protective nets, anti-fall devices, etc. | |
| Precautions for safe operation | Strictly abide by safety operating procedures and eliminate violations |
| Dedicate yourself to work, stay focused and cautious, pay attention to the operation status of the equipment and changes in the surrounding environment | |
| Stop working immediately when potential safety hazards are discovered, and take scientific and reasonable measures to eliminate or avoid them. | |
| Emergency response measures | Formulate detailed emergency response plans, clarify specific processes, division of responsibilities, and rescue measures, etc. |
| In response to emergencies such as equipment failures, fires, and casualties, we will deal with them quickly and effectively to reduce losses. |
Safety operation procedures implementation details table
| Execution | Detailed description |
| Training and assessment | Provide professional training courses covering equipment principles, operating skills, etc. |
| Organize regular assessments to ensure that operators meet the standards of independent, accurate and efficient operation | |
| Environmental maintenance | Clean up the work area daily and keep it clean and orderly |
| Regular inspection and maintenance of heavy equipment tracks to ensure smooth operation | |
| Regularly check the integrity and clarity of safety warning signs and replace damaged or blurred signs in a timely manner | |
| Operation specification | Formulate detailed safety operation procedures, clarify the operation process and precautions |
| Emphasize the operator’s concentration and prudence in work to avoid violations | |
| Establish a safety hazard reporting mechanism to encourage operators to report and deal with potential safety hazards in a timely manner | |
| Emergency response preparation | Formulate emergency response plans and clarify the responsibilities and division of labor of personnel at all levels |
| Organize emergency drills regularly to improve emergency response capabilities and coordinated combat capabilities | |
| Ensure the integrity and availability of emergency equipment and supplies for rapid use in emergencies |
A regular maintenance plan is a critical measure to ensure the normal operation of equipment and extend its service life. To develop a detailed maintenance plan, a comprehensive analysis of the equipment is required to identify key components and wear-prone parts, followed by the formulation of corresponding maintenance measures. For example, for the electrical system, it is necessary to regularly inspect the connections and wear of components such as wires, switches, and relays, and promptly replace damaged parts. For mechanical components, regular inspections of bearings, gears, belts, and other parts are required to ensure stable and reliable operation. Additionally, the effectiveness of safety protection devices must be regularly checked to ensure compliance with safety standards. The lubrication system, being a vital part of the equipment, requires regular inspection of lubricant quality and oil passage conditions, with timely replacement of lubricants to maintain optimal lubrication. Through regular maintenance, potential issues can be identified and resolved promptly, ensuring the equipment remains in good condition, thereby improving production efficiency and product quality.
Troubleshooting and repairing common faults are essential aspects of equipment maintenance. To ensure normal operation and avoid impacts on operational efficiency, it is important to be familiar with methods for identifying and repairing common faults. For instance, for electrical faults, one must master troubleshooting techniques for common circuit and motor issues, enabling quick and accurate diagnosis and effective repair measures. For mechanical faults, understanding repair methods for common gearbox and bearing issues is crucial, allowing for timely replacement of damaged parts and restoration of normal operation. During troubleshooting and repair, safety precautions must be observed, adhering to operational procedures and safety standards to ensure the safety of personnel and equipment. Environmental protection must also be considered to avoid pollution or damage. Timely troubleshooting and repair ensure the equipment operates normally, preventing production interruptions and quality issues caused by equipment failures, thereby enhancing production efficiency and product quality.
Component replacement and upgrades are vital aspects of equipment maintenance. With prolonged use, some components may wear out or become damaged, necessitating timely replacement. Additionally, based on equipment performance requirements and technological advancements, certain components can be upgraded to enhance performance and operational efficiency. When replacing or upgrading components, compatibility, reliability, and durability with the original equipment must be ensured to avoid affecting normal operation. Adequate preparation is required for smooth and effective replacement or upgrades, including understanding the equipment’s principles and structure, mastering relevant tools and skills, and preparing necessary components. Attention to detail, such as tool selection and usage, component models, and specifications, is essential. Strict adherence to operational procedures and safety standards is necessary during replacement or upgrades, with a focus on personal safety and environmental protection. Timely replacement of damaged components and upgrades can improve equipment performance and operational efficiency, extend service life, reduce maintenance costs, and enhance production efficiency and product quality.
Maintenance records and documentation management are crucial aspects of equipment maintenance. Establishing a detailed system for maintenance records and documentation allows for comprehensive monitoring of equipment operation and maintenance status. Recording details such as maintenance time, content, personnel, and results provides a historical reference for future maintenance. Documentation management enables the aggregation and analysis of operational data and maintenance history, supporting decision-making for equipment management. Analyzing maintenance records helps identify potential issues and faults, preventing equipment failures or damage. Reviewing repair documentation summarizes maintenance experience, optimizes repair processes, and improves efficiency and quality. Analyzing operational data assesses equipment performance, predicts maintenance needs, and supports equipment upgrades. Finally, training and educating maintenance personnel enhance their skills and sense of responsibility, ensuring the quality and efficiency of equipment maintenance.
As a highly efficient and stable lifting device, the rail-mounted container gantry crane is equipped with multiple key components to ensure comprehensive functionality and safe operation. The electrical control system, being the core of the crane, incorporates advanced control technology and complete electrical components, enabling precise and reliable operation and control. To enhance operational safety, the crane is equipped with a series of safety protection devices, such as limit switches, emergency stop buttons, and anti-tipping devices, effectively preventing safety hazards caused by improper operation or accidents. Additionally, the lubrication system, an essential component, adopts a fully enclosed, circulating lubrication method and includes specialized tools for regular maintenance and inspection. These standard accessories, rigorously selected and tested, are perfectly integrated with the main equipment, offering stable and reliable performance, and providing strong support for daily operations and maintenance. Users must strictly follow the manual’s instructions for proper use and maintenance of accessories to ensure normal operation and extend the equipment’s service life.
To meet the personalized needs of different customers in various complex working conditions, we offer a wide range of optional accessories. Among these, the remote monitoring system is a significant option, allowing customers to monitor equipment operation status and production data in real-time, improving management efficiency and production safety. Additionally, the intelligent navigation and automatic positioning systems are optional accessories that significantly enhance the operational efficiency and precision of the container gantry crane, reducing labor costs and operational difficulty. When selecting these optional accessories, customers should consider factors such as performance, price, and compatibility with the equipment. Performance is the primary consideration, and customers should choose accessories based on their actual needs. Price is another factor, and compatibility must also be considered to ensure seamless integration with the equipment.
For rail-mounted container gantry cranes, some accessories may require replacement as usage time increases and wear progresses. To ensure a smooth replacement process, the manufacturer provides detailed replacement and installation guides for each accessory. Before replacement or installation, thorough preparation is necessary, including gathering all required new accessories, tools, and other necessary equipment. The process of removing and installing accessories must strictly follow the manufacturer’s guidelines, with each step performed accurately and correctly. Special care must be taken during the removal of old accessories and installation of new ones to avoid secondary damage to the equipment. After installation, necessary debugging and inspection steps are crucial to confirm that the new accessories meet design requirements and standards.
Contact our crane specialists
Send us a message and we will get back to you as soon as possible.