As an indispensable equipment in modern industry, the safety and technical requirements of lifting machine spreaders are directly related to the safety and efficiency of production operations. The spreader not only carries the weight of goods, but also plays a vital role in the complex operating environment. From design to manufacture, to installation, use, maintenance and even end-of-life replacement, every step of the process needs to strictly comply with safety specifications. This is not only to prevent accidents, but also to protect the lives and properties of personnel safety, improve production efficiency. Therefore, in-depth discussion of lifting machine spreader safety technical requirements, to ensure the safe and stable operation of industrial production is of great significance.

Material selection is the cornerstone of spreader design and manufacture, and its rationality directly determines the safety performance and service life of the spreader. When selecting materials, the specific application scenario of the spreader, the characteristics of the working load and the environmental conditions in which it is located must be fully considered to ensure that the selected materials are able to withstand long-term stress loads without damage. For heavy load spreader, especially those need to work in high temperature, high humidity, corrosive environment spreader, should give priority to the selection of high-strength, excellent corrosion resistance and wear resistance of special alloy steel or stainless steel and other high-performance materials. These materials not only have excellent mechanical properties, can resist high strength load, but also has excellent fatigue resistance, can be in a long time under high load operation to maintain stable mechanical strength, effectively prevent the fatigue caused by crack expansion and fracture and other problems.
In terms of strength design, the key components of the spreader, such as lifting beams, lugs, hooks, etc., should be strictly calculated and verified according to the relevant national or industry standards. During the design process, it should be ensured that the safety coefficients of all components meet the specified requirements, e.g., according to the international common specification, for the important components of lifting machinery, their minimum safety coefficients are usually between 4:1 and 6:1. This means that under the design load, the actual load carrying capacity of the component should be at least 4 to 6 times of the design load, so as to ensure that the spreader will not be damaged under extreme conditions and to effectively prevent safety accidents caused by overloading.
The advantages and disadvantages of the manufacturing process directly affect the quality and service life of the spreader. In the manufacturing process, the quality of raw materials should be strictly controlled to ensure that there are no cracks, inclusions and other defects. During processing, advanced technology and equipment, such as precision casting, forging, welding, etc., should be used to ensure the dimensional accuracy and shape tolerance of the spreader. In addition, the finished products need to be strictly inspected and tested, including non-destructive testing, mechanical properties test, etc., to ensure that the quality of the spreader meets the design requirements. Non-destructive testing is a commonly used technical means to assess the internal structure and surface condition of materials. By adopting various methods, such as ultrasonic, magnetic particle and penetration, the key components of the spreader are comprehensively inspected in order to find out the possible existence of tiny cracks, inclusions or other potential defects. Mechanical performance test is to simulate the loading and stress state under actual working conditions, and conduct tensile, compression, bending and other mechanical performance tests on spreader materials or finished products to verify whether they meet the design requirements and national standards. These advanced processes and strict quality control measures can ensure that the spreader is not damaged during the manufacturing process and has sufficient strength and durability, thus providing a strong guarantee for the subsequent safe use.
Safety protection devices are an important and indispensable part of spreader design, and their core objective is to prevent all kinds of potential safety risks and accidents. At the design stage, the designer needs to fully consider the various extreme conditions and risk factors that may be encountered in the actual application of the spreader, including but not limited to overloading, decoupling, collision, over-winding and other dangerous working conditions. In response to these risks, the designer will carefully set up a series of efficient and reliable safety protection devices. For example, the overload limiter is a key device that monitors the actual load weight of the spreader in real time and compares it with the preset rated load. Once the load is detected as exceeding the safety threshold, the overload limiter immediately triggers an alarm system and automatically cuts off the power supply source, thus effectively preventing mechanical damages or safety accidents triggered by overloading; and the anti-delinking device adopts advanced mechanical locking principle or intelligent sensor technology to ensure that the hook is not damaged during operation. The anti-dehooking device adopts advanced mechanical locking principle or intelligent induction technology to ensure that the hook is always reliably connected with the sling during operation to avoid accidental dislodgement leading to material fall or equipment damage.
In addition, for possible collision accidents, the designer will consider setting up anti-collision devices, such as infrared sensors or ultrasonic distance sensors and other equipment, to issue an early warning when the spreader is close to an obstacle and automatically adjust the trajectory or speed of operation; and for potential risks such as over-reeling of the winch or skidding, the designer will design protective measures such as limit switches and emergency braking systems. The use of these safety protection devices can greatly reduce the safety hazards and the possibility of accidents during the lifting operation.
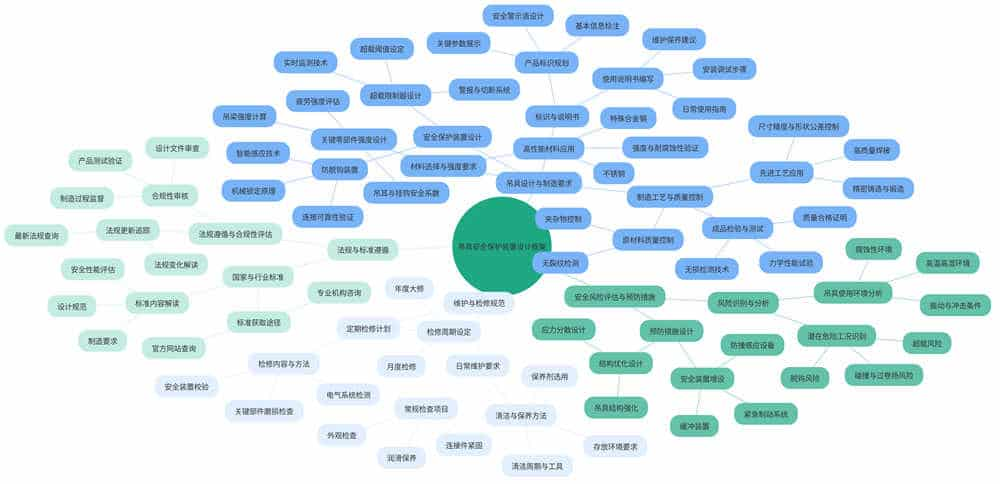
Spreader marking is an important way for users to recognize product information, usage and safety warnings. During the product design stage, the designer needs to carefully plan and determine the content, form and location of the markings. These markings should include, but are not limited to: basic information such as spreader model, specification, manufacturer’s name and date of manufacture; key parameters such as maximum working load; and safety operation tips and warnings. To ensure that the user can quickly access the necessary information and follow the correct operating procedures, the designer also needs to provide a detailed instruction manual. This manual should cover the installation and commissioning steps, daily use precautions and maintenance methods of the spreader.
Before installing the spreader, it is necessary to read the product manual and installation drawings to understand the structure, performance and installation requirements of the spreader. This helps to provide necessary guidance and reference for the subsequent installation work. It is also necessary to investigate the installation site to ensure that the installation location meets the design requirements and to check whether the surrounding environment is safe and free of obstacles. At the same time, prepare the required installation tools, equipment and materials according to the installation requirements, and check whether their quality and quantity meet the requirements.
During the installation process, it is important to operate in strict accordance with the product specification and installation drawings. This includes following the correct installation sequence and steps, as well as ensuring that the installation position, angle, height and other parameters of the spreader meet the design requirements. When installing key components, such as lifting beams and hooks, necessary checks and measurements need to be made to ensure their installation accuracy and reliability. In addition, attention needs to be paid to safety issues during installation. For example, it is necessary to prevent the occurrence of accidents such as falling from height and electric shock to ensure the safety of the staff.
After the installation is completed, the spreader needs to be debugged and inspected. Debugging includes gradually loading to the rated load, observing the deformation and vibration of the spreader to ensure that it works smoothly and without abnormality. Inspection includes comprehensive testing of various performance indexes of the spreader, such as load carrying capacity, stability, safety, etc. Through these tests and verifications, it can be ensured that the spreader meets the design requirements and usage needs.

Before using the spreader, it must be ensured that the operator has fully understood and mastered the correct use of the spreader. This includes, but is not limited to, the structural design principles, functional characteristics and operating procedures of the spreader, etc. The operator not only needs to be familiar with the theoretical knowledge, but must also undergo professional skills training and assessment, and can only be formally put into operation after passing the strict training and obtaining the qualified certificate.
In the actual operation process, especially when performing lifting operations, operators must maintain a high degree of concentration and pay attention to the working condition and performance of the spreader at all times. This means that they have to closely observe whether key parameters such as the spreader’s trajectory, speed control and load carrying capacity are within the normal range, and whether various safety protection devices such as overload protection and limit switches can function properly. Once any abnormal signs or potential risks are detected, such as unstable spreader operation, excessive wear and tear of components, alarms of electronic control systems, etc., they should stop the operation immediately to ensure the principle of safety first and report the problem to the relevant management personnel in a timely manner, so that professional overhaul and maintenance can be carried out.
Daily maintenance of the spreader is the key to ensure its long-term stable operation. The spreader should be cleaned, lubricated and fastened regularly to eliminate potential safety hazards. Regular cleaning of the spreader removes dust, dirt and other debris and avoids wear and damage to the spreader from debris. Lubricating the spreader reduces friction, protects the mechanical equipment and bearings and other components of the spreader, and extends its service life. Fastening the spreader can ensure its structural stability and safety and avoid accidents caused by loosening. At the same time, it is also necessary to carry out regular inspection of the key parts of the spreader, such as wear, deformation, cracks, etc., and should be replaced or repaired in time once any abnormality is found. Periodic inspection of the key components of the spreader is an important measure to ensure its normal operation.
In addition to routine maintenance, the spreader should be inspected and evaluated regularly. The inspection includes the structural integrity of the spreader, the stability of its performance, and the effectiveness of the safety protection devices. When assessing the spreader, it is necessary to make a comprehensive evaluation of the safety performance of the spreader according to the results of the inspection, in order to determine whether it meets the requirements for continued use. If a spreader is found to have hidden safety hazards or performance problems, timely measures should be taken to deal with them, including repair, replacement or scrapping. Periodic inspection and evaluation is an important means of ensuring the safe use of spreaders and must be strictly enforced.
Spreader Periodic Inspection and Maintenance Record Sheet
| Check date | Check items | Check content | Check results | Maintenance measures | Responsible person |
| _ | Structural design integrity | Whether the spreader structure is complete and free of deformation, cracks, etc. | _ | _ | _ |
| _ | Functional characteristics | Whether the spreader function is normal, such as lifting, rotating, etc. | _ | _ | _ |
| _ | Safety protection device | Are overload protection, limit switches, etc. working properly? | _ | _ | _ |
| _ | Wear of key components | Wear degree of wire ropes, pulleys, bearings and other components | _ | _ | _ |
| _ | Electrical system | Are cables, motors, controllers, etc. normal? | _ | _ | _ |
| _ | Cleanliness | Is the surface and interior of the spreader clean and free of debris? | _ | Cleaning spreader | _ |
| _ | Lubrication condition | Whether each lubrication point is well lubricated and there is no dry grinding phenomenon | _ | Lubricating spreader | _ |
| _ | Fastening situation | Whether the connection parts are tight, no loosening phenomenon | _ | Fasten the connection part | _ |
| _ | Comprehensive assessment | Does the spreader meet the requirements for continued use? | _ | Repair/replacement/scrap | _ |
Spreader Maintenance and Repair Record Sheet
| Maintenance date | Maintenance items | Maintenance content | Maintenance results | Note | Responsible person |
| _ | Cleaning and maintenance | Remove dust and dirt on the surface and inside of the spreader | _ | _ | _ |
| _ | Lubrication and maintenance | Lubricate each lubrication point and add lubricant | _ | _ | _ |
| _ | Fastening and maintenance | Check and tighten each connection part to ensure stability | _ | _ | _ |
| _ | Parts replacement | Replace severely worn parts, such as wire ropes, pulleys, etc. | _ | _ | _ |
| _ | Electrical system inspection | Check whether the cables, motors, controllers, etc. are working normally | _ | _ | _ |
| _ | Safety protection device inspection | Check whether overload protection, limit switches, etc. are working normally | _ | _ | _ |
| _ | Functional testing | Test whether the functions of lifting and rotating the spreader are normal | _ | _ | _ |
| _ | Overall assessment | Evaluate the overall performance of the spreader and make suggestions | _ | _ | _ |
Spreaders will be affected by various factors such as wear and tear, aging, corrosion, etc., which will lead to the gradual deterioration of their performance during long-term use. When the spreader has the following defects such as serious wear, deformation, cracks, etc., or when it is found that its key performance indexes such as load carrying capacity, stability, etc. can no longer meet the use requirements, it should be judged as end-of-life. For spreaders exceeding the designed service life, they should also be considered for scrapping.
When replacing the spreader, it should be operated in strict accordance with relevant regulations and procedures. First of all, the new spreader should be accepted and inspected to ensure that its quality meets the design requirements. During the acceptance and inspection process, attention should be paid to the material, size, connection method and other key parameters of the spreader to ensure that it meets the design requirements and safety standards. Secondly, during the replacement process, it should be ensured that the connection methods and sizes of the new and old spreaders are matched to avoid safety accidents caused by improper connection. At the same time, it should be ensured that the operation standardization in the replacement process, to avoid the safety hidden danger caused by improper operation. Finally, after the replacement is completed, the new spreader should be debugged and inspected to ensure that it can work normally and meet the use requirements. In the commissioning and inspection process, attention should be paid to the stability of the spreader, load capacity and other key performance indicators to ensure that it meets the safety standards and use requirements.
For the end-of-life spreader, it should be handled properly. First, it should be removed from the work site and transported to a designated place for storage. During the dismantling process, the safety of the operators should be ensured to avoid injuries caused by improper operation. At the same time, the end-of-life spreader should be transported to the designated location for storage, in order to avoid it being misused or causing environmental pollution. Secondly, the end-of-life spreader should be dismantled or crushed to prevent it from being misused or causing environmental pollution. In the process of disintegration or crushing, corresponding safety measures should be taken to avoid safety accidents caused by improper operation. Finally, the disposal process of end-of-life spreaders should be recorded and archived for subsequent review and audit. The records should include the name, specification, quantity, disposal time and location of the end-of-life spreader for subsequent review and audit. At the same time, the records should be archived for subsequent inspection and audit.
In summary, the safety technical requirements of lifting machine spreaders cover various aspects such as design, manufacture, installation, use, maintenance and scrapping. Only in strict accordance with these requirements for operation and management, in order to ensure that the spreader in a variety of working conditions can be stable and reliable operation, so as to protect the safety of operators and production efficiency. At the same time, it should also strengthen the maintenance and repair work of the spreader to prolong its service life and improve the safety of use.
Contact our crane specialists
Send us a message and we will get back to you as soon as possible.